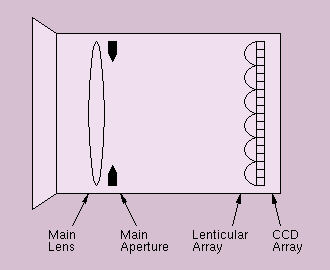
Plenoptic Camera
This Demo is created by John Y. A. Wang

The image behind the lenticular array is digitized to obtain a digital plenoptic image. As a result, each sub-image is represented by a localized array of pixels that encodes the path of light rays entering the main aperture. For a large aperture, various pixels of each sub-image will be lit in the sub-image. For a small aperture, only one pixel will be lit.
|
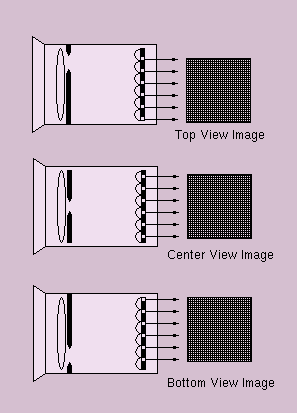
This figure illustrate how views from the top, center, and bottom of
the camera aperture can be obtained by electroniclly selecting the
appropriate pixels from the plenoptic image. Consider a camera with an aperture that activate only one pixel behind each lenticular element. As this aperture is translated, it activate different pixels. For example, forming an image from the lower pixels correspond to a top view. Likewise, forming images from the central pixels or the upper pixels correspond to center and bottom views, respectively. Thus by using a wide open aperture, all views are captured simulatneously by the plenoptic image without any movement of the aperture or camera components. The optics of the plenoptic camera and the arrangement of pixels allow these views to be electronically decoded for recovery of 3D scene structure.
|
The plenoptic camera is self-calibrating and requires only a single-lens camera. It provides views along both the vertical and horizontal axis to recover structure of any orientation. Furthermore the novel optics eliminates spatial aliasing, correspondence and aperture problems, and temporal aliasing problems present in conventional stereo and structure from motion.
| . | . | ![view[1][3]](./images/small/pyry-data0.jpg)
| . | . |
| . | . | ![view[2][3]](./images/small/pyry-data1.jpg)
| . | . |
![view[3][1]](./images/small/pyrx-data0.jpg)
| ![view[3][2]](./images/small/pyrx-data1.jpg)
| ![view[3][3]](./images/small/pyrx-data2.jpg)
| ![view[3][4]](./images/small/pyrx-data3.jpg)
| ![view[3][5]](./images/small/pyrx-data4.jpg)
|
| . | . | ![view[4][3]](./images/small/pyry-data3.jpg)
| . | . |
| . | . | ![view[5][3]](./images/small/pyry-data4.jpg)
| . | . |
In this example, we obatined a 5x5 array of images by electronic decomposition of a single plenoptic image. Show here are the images corresponding to views that would be seen along the vertical and horizontal axes of the camera aperture.
Movies made from these images dramtically show the effects of parallax.
|
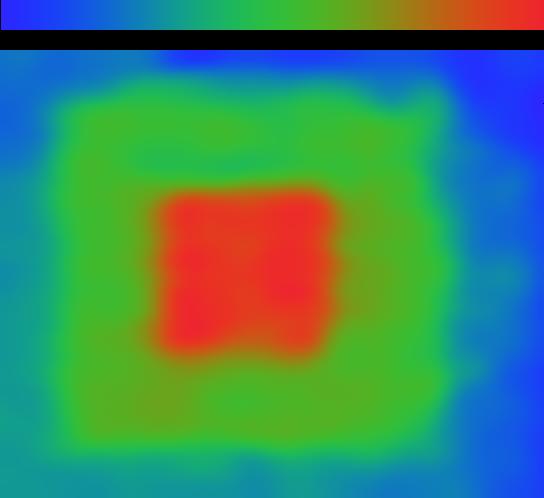
This color range map shows three distinct depth levels corresponding to Lego pyramid obtained by processing 25 views captured by the plenoptic camera. The blue colors indicate points farther from the camera and the red colors indicate points closer to the camera. The color bar show their relative distances.